Antrodia
Taiwanofungus camphoratus
Antrodia is an interesting and unique functional mushroom native to Taiwan. Ecologically, it is parasitic and grows exclusively on the inner heartwood of the endangered Cinnamomum kanehirai tree, also known as the stout camphor tree. This tree is endemic to Taiwan, where the fungus has traditional use and is now highly valued.
Before articificial cultivation was developed, it competed as the most expensive mushroom on the planet. It is also known by several other names, including: Niu-chang-chih , Antrodia cinnamomea, Antrodia camphorata, Stout camphor mushroom. While this fungus was originaly in the genus Antrodia, it has now been relocated as a member of the genus Taiwanofungus. Despite this change, Antrodia is still the name commonly applied to this species. In the wild, this species is protected under law and anyone harvesting or distributing wild-harvested it is subject to heavy penalties.
How Does It Work?
Taiwanofungus contains a diverse array of bioactive compounds that contribute to its various health benefits. These compounds work synergistically to support the body’s natural defenses and promote overall well-being. It is most valued for its anti-cancer properties, aswell as its ability to help protect the liver.The mechanisms of action include:
-Immunomodulation: Taiwanofungus can enhance the immune system by stimulating the activity of various immune cells, such as natural killer (NK) cells, T cells, and macrophages.
–Anti-inflammation: The bioactive compounds in Taiwanofungus can help to reduce inflammation throughout the body, which is a key factor in many chronic diseases.
–Antioxidant activity: Taiwanofungus is a rich source of antioxidants, which protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
-Liver protection: Taiwanofungus has been shown to protect the liver from damage caused by toxins, alcohol, and certain medications.
-Anti-cancer effects: Some studies suggest that Taiwanofungus may have anti-cancer properties, but more research is needed in this area.
Beta-Glucans
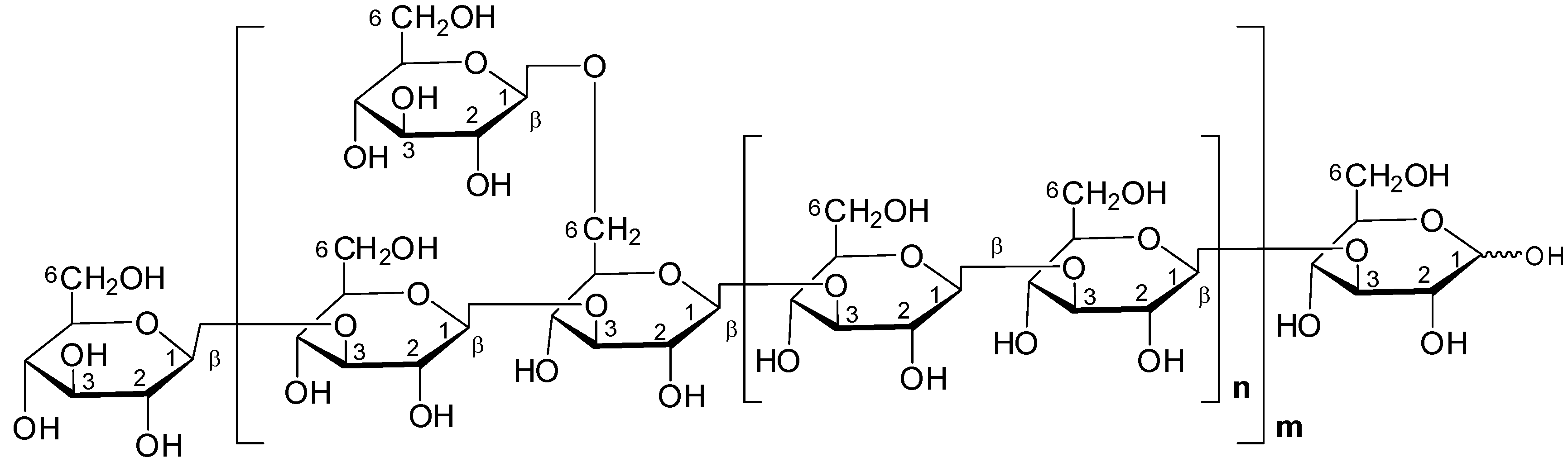
These complex carbohydrates have immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. While all mushrooms contain beta-glcuans, those in Taiwanofungus are particularly potent.
Triterpenoids
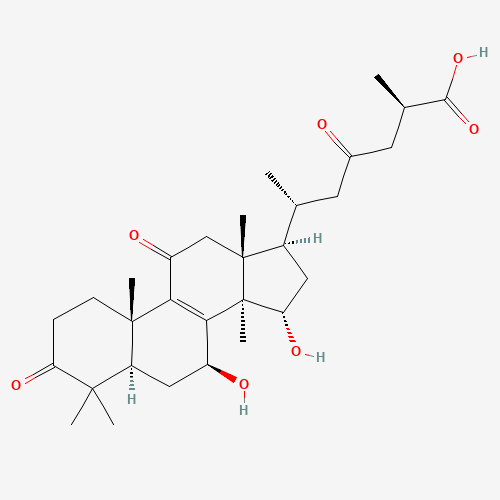
Taiwanofungus is rich in triterpenoids which have anti-inflammatory, liver-protective, and anti-cancer effects. The most well known triterpenoids isolated from Taiwanofungus include antcin A, B, C.
Antroquinonol
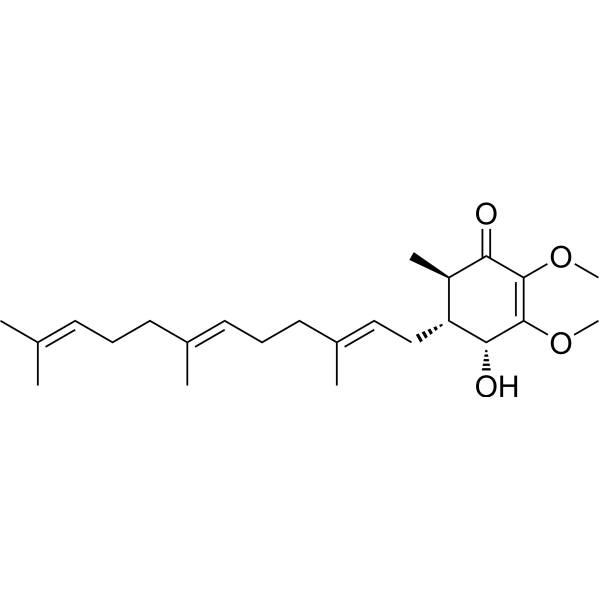
Antroquinonol (ANQ) is a ubiquinone derivative that is unique to Taiwanofungus. It has been shown to have many health benefits, but has been primarily studied in cancer research.
Other Bioactive Compounds
Phenolic Compounds: Powerful antioxidants that protect cells and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Ergosterol: A precursor to vitamin D2, supporting bone health and immune function.
Adenosines: May improve blood circulation, heart function, and cellular energy production.

Clinical Trials
Numerous studies have investigated the potential health benefits of Taiwanofungus. While most of the research has been conducted in vitro or in animal models, there is growing clinical evidence to support its traditional uses. Some of the key findings include:
Improved liver health: Clinical trials have shown that Taiwanofungus can improve liver function in people with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and chronic hepatitis C.
Reduced blood pressure: Taiwanofungus has been shown to lower blood pressure in people with mild hypertension.
Improved sleep quality: A study found that Taiwanofungus improved sleep quality in people with advanced cancer.
Reduced cholesterol: Some evidence suggests that Taiwanofungus may help to lower cholesterol levels.
Note that a large majority of products utilized today are derived from mycelium. This is either cultivated via liquid or solid state fermentation (myceliated grains).