Reishi Mushroom
Ganoderma lucidum
Reishi (Ganoderma linghzi) is one of the most studied and widely used functional mushrooms on the planet. It has been used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for thousands of years, where it’s believed to improve longevity, youth, and overall vitality.
Modern research has revealed that the Reishi mushroom contains a variety of bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, triterpenoids, and antioxidants, that may be responsible for its purported health benefits. It’s immune-boosting properties have been of particular interest to researchers, especially in the context of cancer therapies. Other studies suggest Reishi may reduce inflammation, protect the liver, improve sleep, and lower blood sugar levels.
Keep on reading to learn about the bioactive compounds, how it works, and what the clinical research says.
Health Benefits Of Reishi Mushroom
Research, including preclinical studies (in vitro, animal) and some human clinical trials, suggests Reishi may possess several potential benefits, primarily attributed to its rich array of bioactive compounds like polysaccharides (especially beta-glucans) and triterpenoids (ganoderic acids). Key areas of investigation include:
- Immunomodulation: Beta-glucans are known to interact with immune cells, potentially enhancing or balancing immune responses.
- Sleep Support: Some studies and anecdotal reports suggest Reishi may promote relaxation and improve sleep quality, possibly via modulation of the nervous system.
- Cardiovascular Support: Preliminary research indicates potential benefits related to blood pressure regulation and cholesterol management.
- Antioxidant Activity: Reishi contains compounds that can help neutralize harmful free radicals, potentially reducing oxidative stress.
- Stress Relief and Anti-Anxiety: Some studies have shown compounds in Reishi mushroom may reduce stress, anxiety, and even relieve some symptoms of depression.
- Other Areas: Research also explores potential roles in liver support, blood sugar management, and adjunct support in oncology (always consult an oncologist). It is crucial to note that while research is promising, robust, large-scale human trials are still needed to fully understand it’s use, dosage, and long-term benefits.
Beneficial Compounds
Beta-Glucans
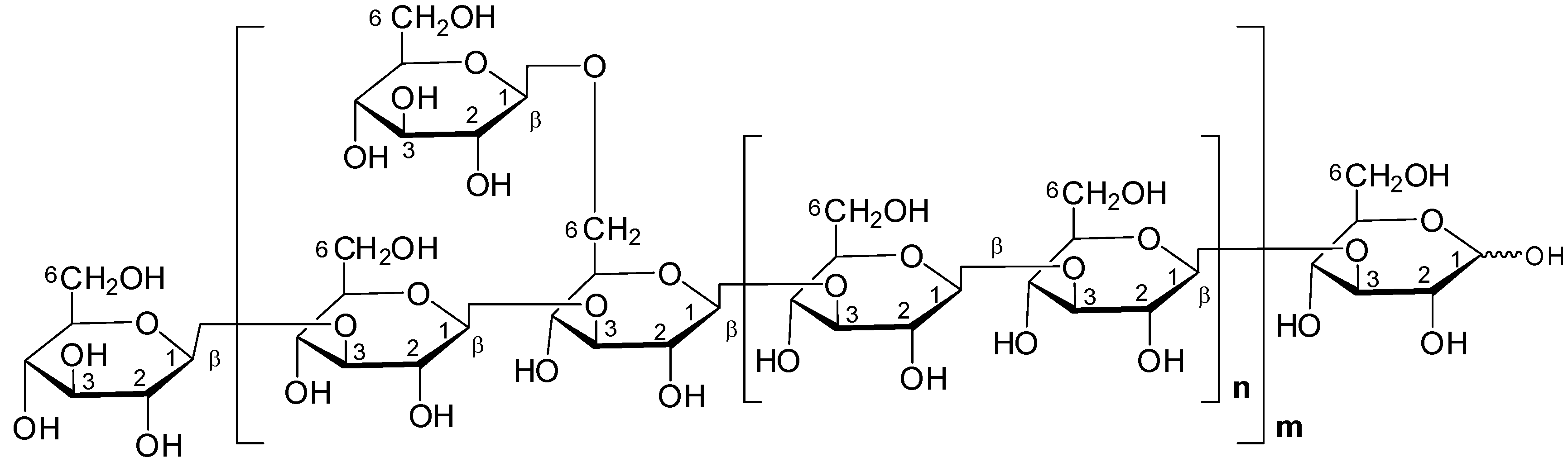
Beta-glucans are a type of polysaccharide that have been studied for their potential to stimulate the immune system and fight cancer cells. Beta-glucans are work by activating various immune cells via specialized receptors, leading to the production of cytokines and other signaling molecules that help to coordinate the immune response. While more research is needed, Reishi polysaccharides may offer promising immunomodulatory and antitumor effects.
Triterpenoids
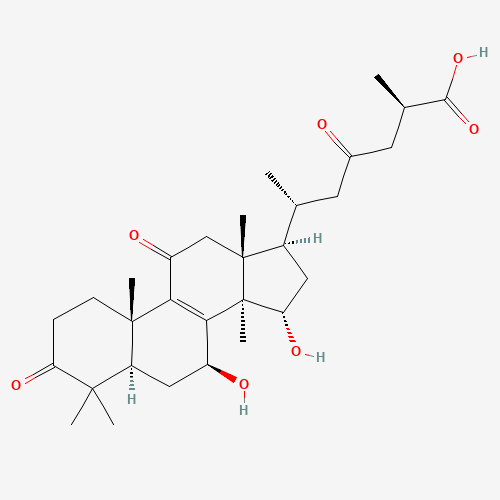
In Reishi mushrooms, triterpenoids are responsible for the mushroom’s bitter taste and have been shown to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and liver-protective effects. They may also help to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Ganoderic acids, a type of triterpenoid found in Reishi, have been specifically investigated for their potential to inhibit tumor growth and metastasis.
Ergosterol
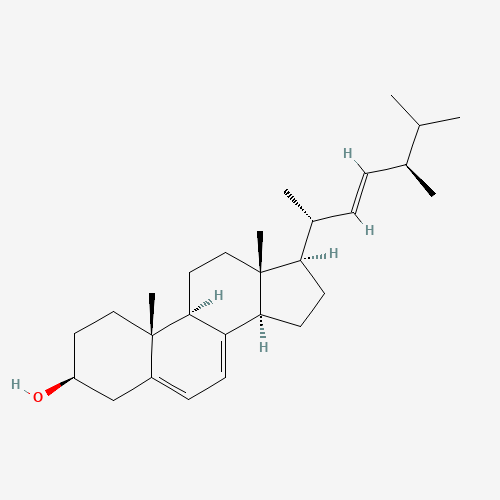
Ergosterol is a natural compound found in mushrooms that has various medicinal benefits. It is a type of sterol that is similar to cholesterol in animals and is a precursor to vitamin D2, which is essential for calcium absorption and bone health. Ergosterol has been shown to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antidiabetic, and neuroprotective effects. It may also help to improve liver health, boost the immune system, and protect against infectious diseases.
Clinical Research Overview
Supporting Liver Function
Clinical trials indicate that Reishi mushroom extracts may be beneficial for liver health. In patients with chronic hepatitis B, an extract called Ganopoly helped reduce viral markers like hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) and hepatitis B viral (HBV) DNA, and also normalized liver enzyme levels such as aminotransferase (ALT) (Gao et al., 2002). Beyond hepatitis, a study in healthy volunteers found that Reishi extract helped reduce hepatic marker enzymes (GOT and GPT) and showed a reversal from mild fatty liver conditions to normal (Chiu et al., 2017).
Improving Immune Function
Reishi is widely recognized for its immune-modulating abilities. Clinical studies have shown that Reishi polysaccharides can enhance the overall immune response in patients, including those with advanced cancer (Gao et al., 2003a;Gao et al., 2003b ). In healthy adults and children, Reishi β-glucans led to a significant increase in the count of various immune cells in the bloodstream, such as total lymphocytes and specific T-lymphocytes (CD3+, CD4+, CD8+), while also boosting immunoglobulin A (IgA) levels and NK cell cytotoxicity (Henao et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2023).
Cancer Treatment Support
Reishi appears to offer supportive benefits in cancer treatment. For patients with advanced solid tumors, including lung cancer and gynecologic cancers, Reishi polysaccharides have helped achieve stable disease in a notable percentage of individuals (Gao et al., 2002; Suprasert et al., 2015). In a study involving early-stage triple-negative breast cancer, Reishi spore powder was suggested to improve overall survival and disease-free survival (Jiang et al., 2024). When used alongside transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for hepatocellular carcinoma, Reishi β-glucan was linked to increased complete and partial treatment responses, tumor shrinkage, improved survival rates, and an increase in immune cells (CD4, CD8, and IL-2) (Poedjomartono et al., 2020). In breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, Reishi also showed an increase in certain immune markers and a decrease in inflammatory markers like TNF-alpha and IL-8, which may enhance treatment effectiveness (Zhao et al., 2011; Deng et al., 2020).
Reducing Fatigue and Improving Well-being
Clinical trials indicate that Reishi mushroom can significantly reduce feelings of fatigue and improve overall well-being. This has been demonstrated in patients with neurasthenia, where it led to a notable reduction in fatigue and an increase in the sense of well-being (Tang et al., 2005). Similarly, for breast cancer patients undergoing endocrine therapy, Reishi spore powder showed improvements in cancer-related fatigue and physical well-being (Zhao et al., 2011). It also showed potential to alleviate fatigue and enhance quality of life in individuals with chronic fatigue syndrome (Sokawatmakhin et al., 2013).
Supporting Mood and Sleep
Reishi may have positive effects on mental well-being and sleep patterns. Patients with breast cancer who took Reishi reported less anxiety and depression (Zhao et al., 2011). In individuals with fibromyalgia, there was an observed trend toward improved happiness, increased satisfaction with life, and reduced depression (Pazzi et al., 2017;Garcia-Gordillo et al., 2020). For elderly subjects with respiratory tract infections, a combination extract including Reishi was associated with a reduced incidence of sleep disturbances, aligning with its traditional use for insomnia (Gracián-Alcaide et al., 2020).
Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
Studies have shown that Reishi can act as a potent antioxidant and help reduce inflammation in the body. In patients with high-risk and stable angina, a Reishi extract significantly reduced markers of oxidative stress (like MDA) and improved endothelial function (Sargowo et al., 2017). In healthy volunteers, Reishi extract boosted the body’s total antioxidant capacity and the activity of antioxidant enzymes while reducing markers of cellular damage (Chiu et al., 2017). It has also been shown to decrease inflammatory markers like TNF-alpha and IL-8 in breast cancer patients (Zhao et al., 2011) and reduce inflammatory factors like IL-6, IL-1beta, and TNF-alpha in hypertensive patients (Sugita et al., 2019). Furthermore, it has shown promise in reducing abdominal pain and improving inflammatory markers in patients with ulcerative colitis when used as an adjunctive therapy (Simadibrata et al., 2023).
Managing Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
Clinical trials have demonstrated that an extract of Ganoderma lucidum can significantly improve symptoms associated with lower urinary tract issues, such as those related to bladder outlet obstruction (Noguchi et al., 2007; Noguchi et al., 2008).
Pain Management
Reishi has shown promise in alleviating pain in various conditions. In patients with active rheumatoid arthritis, a combination therapy that included Reishi provided significant analgesic (pain-relieving) effects, leading to improved pain scores (Li et al., 2007). It has also demonstrated an analgesic effect in fibromyalgia patients (Pazzi et al., 2017; Garcia-Gordillo et al., 2020). Furthermore, a pilot study found that Reishi extract helped relieve painful symptoms in patients with Restless Legs Syndrome (Bugnicourt, 2023).
Skin Health Improvement
In a multiple-case study, Reishi was found to be a useful adjunctive treatment for severe atopic dermatitis. It led to noticeable alleviation of symptoms such as itching, flare, swelling on the face/skin, and improved excoriations and lichenification on the trunk and extremities (Honjo et al., 2015).
Potential Antiviral Activity
A preliminary clinical trial involving a combination of Reishi and another medicinal mushroom (Trametes versicolor) demonstrated a significant clearance of oral human papillomavirus (HPV) serotypes 16 and 18 (Donatini, 2014). Additionally, in elderly subjects, a combination of elderberry and Reishi extracts was associated with a reduced duration of common cold events and a lower probability of high severity influenza-like illness, suggesting antiviral potential (Gracián-Alcaide et al., 2020). In COVID-19 patients, Ganoderma lucidum was observed to have a significant role in reducing the COVID-19 malicious effect on studied hematological parameters (Al-dulaimi et al., 2020).
Clinical Trials
The clinical trials conduct on Reishi highlight the diverse applications of reishi, ranging from cancer support to metabolic health and immune modulation. They utilized various forms of reishi, including spore powder, extracts, and whole mushroom preparations.

Reishi Mushroom Dosage Guidelines
Like any drug or herbal medicine, dosage is a key component to effective treatment. When it comes to Reishi mushroom dosages, these can vary widely depending on the form in which your consuming it and your specific condition. Generally speaking, dosages vary anywhere from 500 mg to over 6000 mg per day for a 1:1 fruiting body extract.
Factors Influencing Dosage
- Potency: Potency refers to how concentrated a product is. More specifically, it can be thought of how many bioactive compounds it contains. For example, beta-glucans (a key bioactive comppound) can range from just a couple percentage points in low-quality products, to 30-40% in good products, and above 80% in highly refined products utilized in clinical settings. We highly reccomend you check out our supplement buying guide to make sure you invest in a good product.
- Condition: Serious conditions generally require larger doses that range up to 3-5 grams (for a good product.) For less serious conditions, or for general well-being, 1 gram is usually reccomended as a base.
- Treatment: While it’s not very well studied, you may choose to take Reishi along with other herbs/medication. While Reishi is regarded as safe and has not been shown to have serious contradictions, the efficacy of mixed treatments has not been well studied.
How Much Reishi Mushroom Should You Take?
- General Well Being and Prevention: 500-1500 mg per day
If all you’re looking for is to improve your well-being or reduce how often you get sick, it’s generally reccomended to consume atleast 1000mg. You can get away with doses aslow as 500 mg but they will be less effective. - Mild to Chronic Conditions: >1000 mg per day
If you are trying to improve a certain condition, such as allergies, bad sleep, irratibility, ect. you should take at least 1000 mg. Taking more may improve results. - Serious Illness: >3000-5000 mg per day
If you are suffering from a serious or potentially life thereatening illness, you should consult your doctor. Reishi on it’s own is not considered a cure for anything, although it could improve the results of certain treatments. Taking over 5000 mg is not unheard of for some illnesses.
Frequently Asked Questions About Reishi Mushrooms
What is Reishi Mushroom?
Reishi, scientifically known as Ganoderma lucidum, is a polypore fungus characterized by its distinct kidney- or fan-shaped, reddish-brown, varnished-looking cap and woody texture. It typically grows on decaying hardwoods. For centuries, it has been used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and other systems for promoting health and longevity. It is now cultivated globally for use in dietary supplements and functional foods.
What Does Reishi Mushroom Feel Like?
Reishi is not a psychoactive substance like stimulant or sedative drugs, nor does it produce euphoria or an immediate, pronounced ‘feeling’ for most users. Its effects are generally subtle and cumulative, often described as promoting a sense of calmness, reduced stress, or enhanced relaxation over time with consistent use. Some individuals may notice improvements in sleep quality. It does not impair cognitive function or cause drowsiness during the day for most people when used appropriately. Effects are highly individual.
How Long Does It Take to Feel the Effects of Reishi?
Reishi’s effects are typically gradual and cumulative, not immediate. As an adaptogen and immunomodulator, its benefits often build over weeks or months of consistent daily use. Subtle effects like improved relaxation or sleep quality might be noticed by some individuals within hours, days or a few weeks.
Does Reishi Have Side Effects?
Reishi is generally considered safe for most healthy adults when taken appropriately. Phase 1 Clinical Studies which investigate safetyness of Reishi have not found any significant side effects or dangers. Some users report dryness of the mouth due to the bitter and slightly astringent nature.
Is Reishi Dangerous?
For most healthy individuals, Reishi is not considered dangerous when sourced responsibly and used correctly. However, caution and avoidance are warranted in specific situations. If you have any serious condition ALWAYS consult your doctor when adding anything into your treament. Please utilize caution if you have a bleeding disorder, are going into surgery, have low blood pressure, autoimmune diseases, are pregenant or breastfeeding, or have allergies.
Is Reishi Hallucinogenic?
No, absolutely not. Reishi mushroom does not contain psilocybin, psilocin, or any other compounds known to cause hallucinogenic or psychedelic effects. It does not alter perception, induce visions, or create the altered states of consciousness associated with “magic mushrooms.” Confusion sometimes arises due to the general term “mushrooms,” but Reishi’s pharmacological profile is entirely different.