
A 1:1 fruiting body extract powder is derived purely from the mature mushroom structure (no mycelium but the fruiting body), containing no fillers (like solvents), and processed via methods like dual extraction to ensure bioactive compounds are available for absorption. These products are ideally presented in a stable powder form.
Its quality and claimed benefits, however, hinge crucially on verification through analytical testing. This article provides a direct explanation of these critical factors, defining why this type of extract, when adequately produced and verified, is foundational for potent and trustworthy mushroom products
What is a 1:1 Fruiting Body Extract?
- Fruiting Body: This refers to the actual mushroom structure that emerges from the substrate, the cap, stem, and gills (or pores/teeth). This is distinct from the mycelium (the root-like network) or, critically, from “mycelium on grain” (MOG), where the mycelium is grown on a grain substrate (like rice or oats) and the entire mass is often ground together. Learn about mycelium on grain products here.
High-quality extracts prioritize the fruiting body, as it typically contains the highest concentration and broadest spectrum of the mushroom’s characteristic beneficial compounds. Using myceliated grain can result in products diluted with significant amounts of residual grain starch. - Extract: An extract is a concentrated preparation derived from the raw mushroom material. The simple grinding of raw mushrooms does not make key compounds bioavailable. Extraction processes are necessary to break down the tough chitin cell walls of mushrooms and isolate the desired bioactive compounds. This makes sure the beneficial compounds are bioavailable, and won’t just “pass through” your organism.
- 1:1 Ratio: This ratio signifies that one part of the extracted material corresponds to one part of the original raw, dried mushroom biomass. For example, 1 kilogram of dried fruiting bodies yields 1 kilogram of 1:1 extract powder. This indicates that the extract represents the natural concentration profile of the mushroom without dilution of specific compounds relative to the starting material. It is not a measure of active compound concentration (like beta-glucans) but rather a statement about the yield relative to the initial biomass. While analytical testing is the only way to confirm the real concentration, it is a good way to make a first judgement on a product.
Powdered vs. Tincture Extracts: Considerations for Quality and Stability
Powdered extracts are generally composed of 100% mushroom fruiting body and nothing else. In most cases, they undergo an extraction with solvents (alcohol/water usually), but these solvents are evaporated. This leaves you with the bioavailable components that were extracted, aswell as the original “fiber” of the mushroom. Tinctures utilize solvents, but the fiber is separated and not utilized in the product. In most cases, this results in significant losses because not everything can be effectively removed from the fiber.
Powders are generally preferred because;
- Stability: Powders are inherently more stable and have a longer shelf life than liquids, which can degrade over time or require preservatives.
- Concentration: It is often easier to achieve verifiable and consistent concentrations of key compounds in a powdered format. Liquid extracts are often less concentrated, as complete
- Purity: Powdered extracts typically do not require preservatives or carriers like alcohol or glycerin, which are common in liquid tinctures and can be undesirable for some users.
- Versatility: Powders are easily encapsulated or incorporated into various formulations and delivery systems.
All of this said, there are always exceptions. There are individuals making highly concentrated tincutres, but these are far and few between.
Analytical Testing: The Non-Negotiable Foundation of Quality
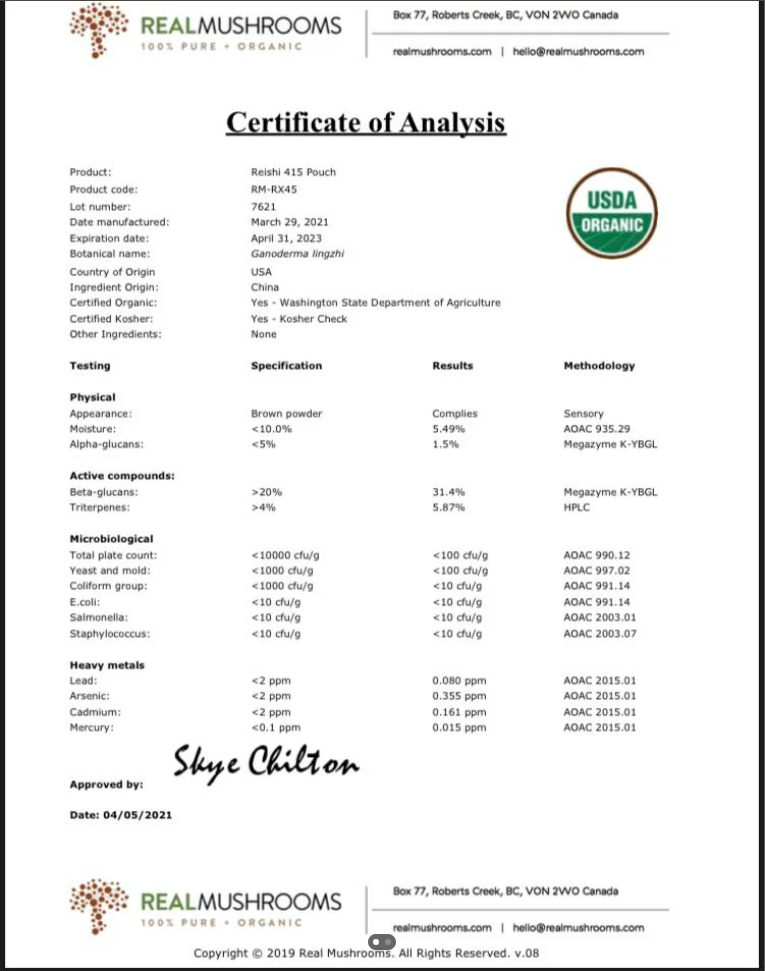
A product labeled “1:1 Fruiting Body Extract” means little without verification. Analytical testing by reputable third-party laboratories is fundamental to confirming the quality, potency, and safety of any mushroom supplement. Key parameters include:
- Compound Quantification: Using methods like High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), testing verifies the presence and concentration of key bioactive compounds (e.g., >25% Beta-Glucans, specific triterpenoid levels). This confirms the extraction was successful and the product meets efficacy standards.
- Identity Verification: Confirming the mushroom species is correct.
- Purity and Safety: Screening for contaminants such as heavy metals (lead, mercury, cadmium, arsenic), pesticides, and microbial load ensures the product is safe for consumption.
- Absence of Fillers: Testing can confirm the absence of undeclared fillers, such as the grain starch often found in MOG products.
Why 1:1 Fruiting Body Extracts Set the Standard
A high-quality 1:1 fruiting body extract, produced using appropriate dual extraction methods, careful drying techniques, and rigorously verified through comprehensive analytical testing, represents a commitment to delivering a product that is:
- Derived from the most valuable part of the mushroom.
- Processed to maximize bioavailability.
- Reflective of the mushroom’s natural compound profile.
- Verified for potency and purity.
In the context of mushroom clinical trials and therapeutic applications, demanding these standards is crucial for ensuring reliable, reproducible results and harnessing the true potential of medicinal mushrooms. Always look for products that transparently provide details on sourcing (fruiting body), extraction methods, and comprehensive third-party analytical results.

No responses yet