How does the Royal Sun Agric work in the ?
The primary active compounds identified in Agaricus blazei are β-glucans and proteoglycans, which interact with the immune system to enhance the body’s ability to respond to infections, inflammation, and potentially cancer. These polysaccharides bind to receptors such as Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), dectin-1, and complement receptor 3 (CR3) on immune cells, stimulating proinflammatory cytokine production.
There are multiple bioactive polysaccharides in Agaricus blazei, with different mechanisms of action. Some of these compounds may play a role in immune modulation, while others have potential anticancer or antiviral effects.
Beta-Glucans
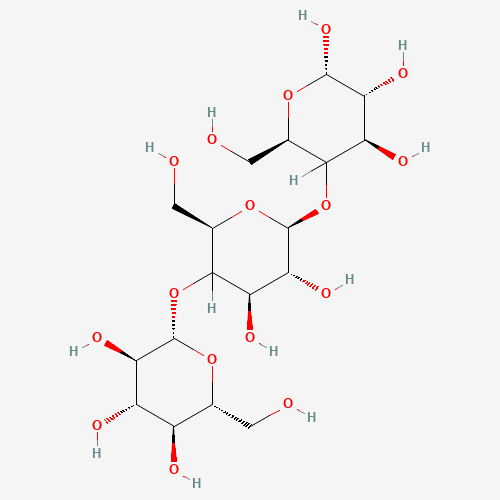
β-glucans are the most well-studied active compounds in Agaricus blazei. They are complex polysaccharides that activate immune cells, particularly macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells, and T-cells. The β-1,3 and β-1,6 glucans found in Agaricus blazei are believed to be responsible for immune stimulation and antitumor activity. Studies suggest that these compounds enhance phagocytosis (the body’s ability to consume and destroy pathogens) and stimulate the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ)
Other Beneficial Compounds
Proteoglycans
These large molecules also contribute to immune stimulation and may have anti-inflammatory effects.
Phenolics
Found in smaller quantities, these compounds act as antioxidants, potentially reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
Erosterol
A precursor to vitamin D2, which plays a role in bone health and immune function
ergothioneine
Ergothioneine is a powerful antioxidant naturally found in mushrooms. It plays a critical role in cellular health and protection, potentially supporting immunity and longevity.
Considerations
Research on Agaricus blazei peaked in the early 2000s, and studies have raised some safety concerns. Liver toxicity has been reported in high-dose users, particularly cancer patients undergoing treatment. The mushroom also contains agaritine, a compound with potential carcinogenic effects in animals, though its impact on humans remains unclear.
Due to its immune-stimulating properties, those with autoimmune disorders or on immunosuppressive drugs should consult a healthcare professional before use. Some individuals may also experience digestive discomfort or allergic reactions. Given the lack of recent clinical research, caution is advised when using Agaricus blazei as a supplement.
